Root Canal Treatment
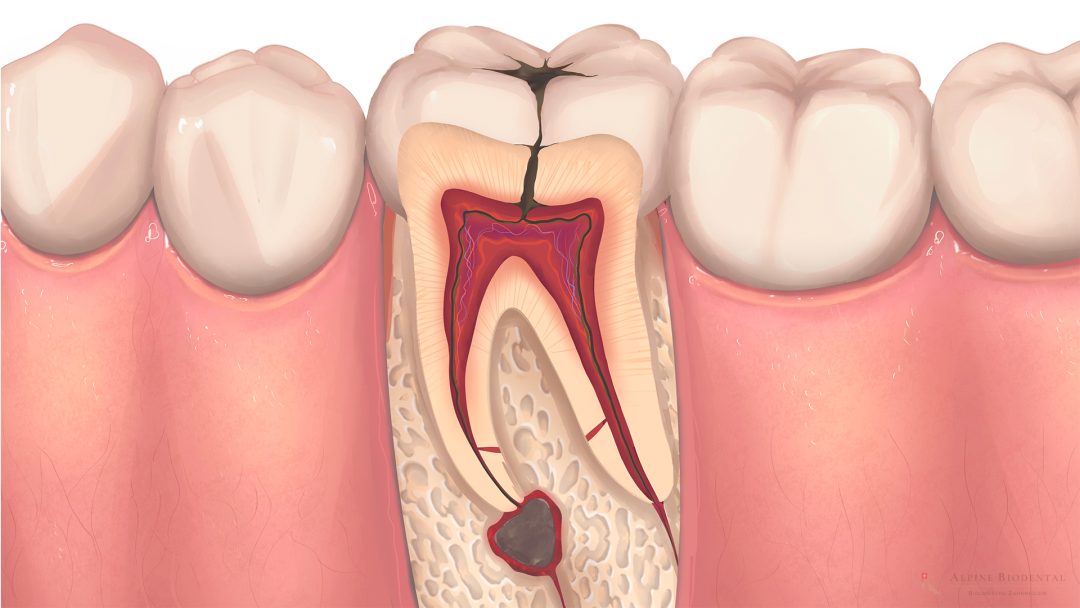
Root canal treatment is a dental procedure in which the tooth nerve is removed from the tooth and filled with a root filling.
In informal language, people often call it dental root treatment, but the precise term is root canal treatment since the procedure focuses on treating the channels within the tooth roots.
What is root canal treatment?
Many people wonder what a root canal treatment is. It is a commonly performed therapy in dental practices where the tooth nerve is removed from the root canals, and the root canals are cleaned and disinfected. X-rays are taken before, during, and after the root canal treatment to monitor the length of the canals and ensure proper execution.
During root canal treatment, the tooth nerve is removed, and the root canals are thoroughly cleaned using both mechanical files and disinfection with antibacterial solutions. Once the tooth is cleaned from the inside, a root filling is placed to seal the tooth completely and prevent the entry of bacteria.
When is root canal treatment performed?
Root canal treatment is performed when deep decay has affected the tooth, causing it to die. In X-rays, one often observes bone dissolution with a dark area around the root tip. This condition is colloquially referred to as tooth root inflammation and is often painful. Root canal treatment can effectively eliminate the pain without the need for tooth extraction.
Root canal treatment procedure
During a root canal treatment, the tooth nerve is removed, and the root canals are thoroughly cleaned using both mechanical instruments and disinfection with antibacterial solutions.
After the tooth is completely cleaned from the inside, a root filling is placed to seal the tooth and prevent bacterial penetration.
Often, a medicated filling is placed as an interim step to ensure the elimination of all bacteria and thorough disinfection.
Duration of root canal treatment
The duration of root canal treatment depends on various factors. The tooth’s anatomy, including the number of root canals, significantly influences the treatment duration. Teeth can have up to 5 root canals, which can extend the treatment time. Many dentists perform root canal treatment with a microscope, which can also lengthen the duration.
Risks of root canal treatment
There are some risks and disadvantages associated with root canal treatment. The complexity of the tooth’s structure, with numerous tiny channels, provides ideal conditions for bacteria to thrive. Additionally, the treatment eliminates the tooth’s nerve, blood supply, and immune defense, allowing bacteria to easily contaminate the tooth structure. Despite thorough root canal cleaning, this situation cannot always be prevented.
Organic tissue in the devitalized, dead tooth is slowly decomposed by microorganisms, producing toxic metabolic by-products that can spread to surrounding tissues and enter the body through blood vessels and nerve strands. Another issue is that each tooth is connected to neuronal pathways (meridians), and a dead tooth can act as a disturbance field, negatively affecting the corresponding meridian and potentially manifesting in physical symptoms.
Pain during and after root canal treatment
Root canal treatment is generally not or only slightly painful, as the tooth is numbed beforehand. However, many patients report pain after completing root canal treatment. In such cases, tooth extraction is usually necessary.
Natural pain relievers can temporarily alleviate the pain.
Tooth discoloration due to root canal treatment
Root-treated, dead teeth are often darkly discolored, posing an aesthetic concern for patients. Tooth bleaching is often ineffective in addressing this discoloration, and covering the dark tooth with a veneer or ceramic crown is commonly necessary.
Cost of root canal treatment
The cost of root canal treatment can vary significantly depending on the number of canals in the tooth. A root canal treatment on a molar tooth typically costs more than on an incisor. There are also differences in cost from dentist to dentist, depending on the treatment plan and execution.
Alternatives to root canal treatment
Due to the risks and drawbacks of root canal treatment, many patients seek alternatives. Currently, the only alternative to root canal treatment is tooth extraction and subsequent replacement with dental prosthetics, such as a ceramic implant or bridge.
Leaving a tooth gap without replacement is associated with various disadvantages, such as neighboring teeth tilting or opposing teeth growing into the gap.
Frequently asked Questions about Root Canal Treatment
The topic of root canal treatment often raises various questions. In this section we would like to give you the answers to frequently asked questions.
It is not uncommon for inflammation in the jawbone to persist despite completed root canal treatment. In such cases, tooth extraction is the ideal course of action.
Root-treated teeth can become unstable and break over time due to increased fragility. If your root-treated tooth has broken, an urgent appointment with the dentist is necessary. The treatment will vary depending on the depth of the fracture.
A root-treated tooth may start to hurt even after several years. This can occur because a chronic infection often remains at the root tip of a root-treated tooth. Depending on the patient’s immune system, the chronic infection can turn into an acute one, causing pain. In such a situation, the affected tooth often needs to be extracted.
Apical surgery is performed to save a painful, already root-treated tooth. During this procedure, the inflamed root tip of the tooth is removed, and the rest of the tooth is left in the jawbone. Since the long-term prognosis of apical surgery is not favorable, tooth extraction should be considered.
The tooth root is the part of the tooth anchored in the jawbone. Teeth can have one, two, or three tooth roots.
The tooth nerve is located in the tooth, specifically in the tooth canals. This tooth nerve consists of nerve fibers, small blood vessels, and lymph vessels. Its role is to supply the tooth with life.
Further information
Further information intended to give a better overview of the topic.