Peri-implantitis - Inflammation around Dental Implants
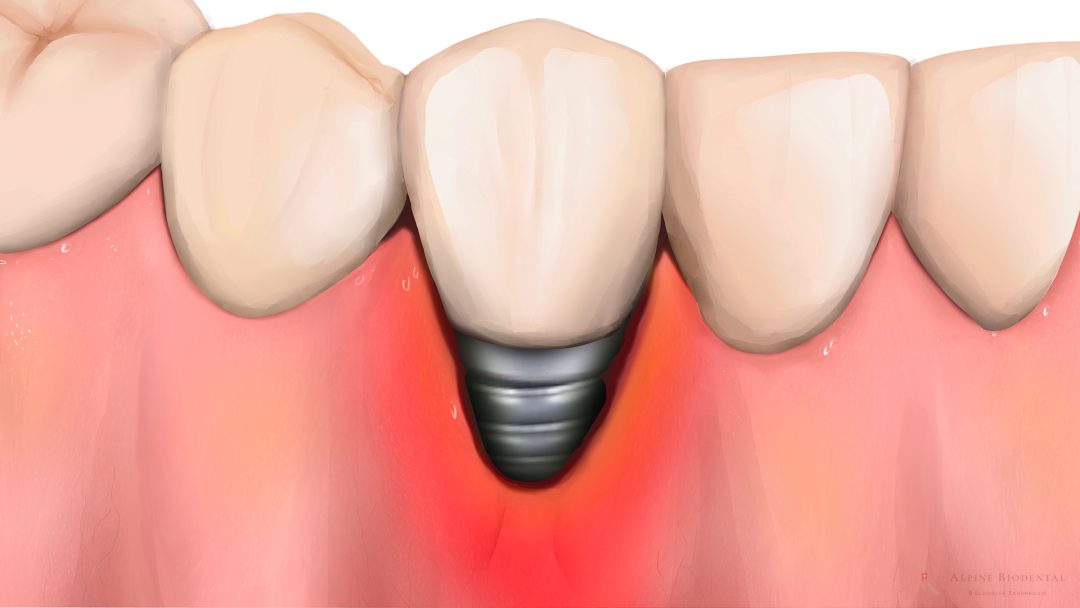
Peri-implantitis is an inflammation of the tissue around the dental implant. The gums and jawbone adjacent to the implant exhibit various signs of inflammation, such as swelling, redness, and pain. If peri-implantitis is not treated, it typically leads to implant loss.
Causes of Peri-implantitis
The causes of peri-implantitis can be diverse and mutually reinforcing in their effects. For instance, a patient with an unhealthy oral flora who also smokes is guaranteed to develop a problem. If there is an additional high concentration of the enzyme aMMP8, all teeth can become loose and fall out within months.
Poor Oral Flora
If there are bacteria in the oral cavity capable of damaging gums and bones, peri-implantitis can develop rapidly. Pathogenic bacteria, for example, produce enzymes that break down the adjacent tissue and destroy implant anchorage.
When these harmful bacteria increase in number and form biofilms and deposits on the dental implant, peri-implantitis is inevitable.
Building a healthy oral flora is crucial and forms the basis for lasting and stable dental health.
Elevated Levels of aMMP8
aMMP8 is an enzyme produced when granulocytes come into contact with bacterial biofilms. This enzyme has the negative property of breaking down peri-implant tissue by splitting the collagen fibers in the gums and jawbone.
For the longevity of the implant, dental health, and overall health, it is crucial that the value is not elevated. Please refer to Periodontitis Diagnostics for more information.
Smoking
Smoking also has a very detrimental effect on the tissue around the implant. Peri-implantitis is very often observed in patients who smoke. Smoke acts as a local poison on the tissue, making inflammation around the implant easily understandable. Additionally, smoking increases the concentration of CO2 in the mouth, causing the pH level to drop into the acidic range. This leads to a shift in the oral flora, significantly affecting peri-implant tissue.
It is strongly recommended to quit smoking before getting implants or ceramic implants.
Vitamin D3 Deficiency
A deficiency in the essential sunshine vitamin D3 is also a contributing factor to peri-implantitis. With a vitamin D3 deficiency, the jawbone is severely affected, leading to inflammatory loosening of implants. Generally, D3 plays a role in numerous processes in the body and is effective in bone, muscle, and immune system function, among other things.
Our dental practice specializes in effectively optimizing the oral bacterial flora. In this process, only harmful bacteria are eliminated, while the healthy and essential bacteria remain alive.
For our patients, we can determine the aMMP8 value within a few minutes. This allows us to identify the risk of future periodontitis or peri-implantitis before the first symptoms appear.
Peri-implantitis and the Impact on Health
Peri-implantitis has a similarly negative impact on health as periodontitis. Through the inflamed tissue, bacteria can penetrate the bones and blood vessels in large numbers, leading to various diseases in the body. Peri-implantitis is associated with diseases such as arteriosclerosis (heart attack, stroke), diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, arthritis, or rheumatism.
Patients often complain of fatigue and lack of energy. This is due to the continuous activation of the immune system, which requires a lot of energy to defend against bacterial invasion.
Treatment of Peri-implantitis
In general, the treatment of peri-implantitis should always involve the bacterial flora, as it is the origin of the problem. This eliminates the destruction caused by problematic bacteria, and the production of aMMP8 significantly decreases.
Cleaning the surface of the affected dental implants can be done as a supportive measure. It is essential to ensure that no unnecessary titanium particles are released into the surrounding area. The more titanium shavings and particles are present in the peri-implant tissue, the more pronounced the inflammatory reaction.
If the breakdown of peri-implant tissue is too advanced, complete healing cannot take place. In severe cases, the dental implant should be removed.
Peri-implantitis and Periodontitis
With peri-implantitis, the inflammation is localized around the implants, whereas with periodontitis, the tissue around the teeth shows inflammation.
Both conditions are symptoms of the same cause. In both peri-implantitis and periodontitis, the main cause is a disease-causing bacterial flora in the mouth. Therefore, the treatment is the same: building a healthy oral flora. The presence of periodontitis increases the risk of developing peri-implantitis after implantation. Patients with periodontitis should improve their oral flora before getting implants and complete the treatment for periodontitis.
Dental Implant Materials
Peri-implantitis also depends on the material from which the dental implant is made. Titanium implants, in the context of peri-implantitis, have various disadvantages. Implants made of ceramic are clearly preferable. In the following sections, you will learn more about what distinguishes the two materials, titanium and ceramic, concerning peri-implantitis.
Peri-implantitis and Titanium Implants
Titanium implants have the property of healing stably, even when inflammation is left during implant placement and the work is not done cleanly. Titanium implants can remain in the jawbone for a long time without loosening, even with peri-implantitis.
As a result, severe inflammation can develop around the titanium implant, and yet the implant remains immobile and stable. The disadvantage is that peri-implantitis can go unnoticed for a long time and can significantly burden the body.
Causes of Peri-implantitis with Titanium
- Implants Titanium implants usually have a gap at the bone edge. This gap can harbor bacterial biofilms and intensify local inflammation.
- Titanium is not rigid but easily deformable. During chewing, microscopic movements in the form of pressure are transmitted to the jawbone. Pressure always leads to tissue breakdown, automatically favoring an inflammatory process.
- When placing titanium implants, titanium particles are always released into the surrounding area. The particles are phagocytized by macrophages in the peri-implant tissue, after which these immune messengers release into the environment. If the macrophages react with an increased immune response, the titanium stimulation test is positive.
Macrophages always respond with an inflammatory response after taking up titanium particles. If you want to know whether this response is mild or severe, you can have a titanium stimulation test performed.
Since titanium also contains elements such as nickel, aluminum, or vanadium, it can be tested whether an allergy to these additives is present. Testing is best done with a lymphocyte transformation test (LTT).
Peri-implantitis and Ceramic Implants
Peri-implantitis can also occur with ceramic implants. If the implantation is done uncleanly and inflammations are not completely removed from the tissue, peri-implantitis can develop, and the ceramic implant will not heal. The implant will lack stability since it cannot osseointegrate. Consequently, it must be removed and re-implanted.
If the insertion of the ceramic implant is done cleanly, and the wound is thoroughly cleaned and disinfected, ceramic implants heal without inflammation in the jawbone.
Reasons for Rare Peri-implantitis with Ceramic Implants
- The design of most ceramic implants does not have gaps, preventing bacterial colonies from settling there.
- Both the gums and the bone like to connect with zirconia ceramic.
- Ceramic is rigid and does not show movement under chewing forces. Therefore, there are no pressure peaks that break down the jawbone.
- From an immunology and toxicology perspective, ceramic is neutral. There is no immune reaction.
If a healthy oral flora is maintained, and daily oral hygiene is correctly performed, ceramic implants can remain in the jaw for many decades without complications.
Dr. med. dent. Rebekka Hueber
Peri-implantitis should be recognized and treated in a timely manner. We are happy to help you.

Frequently asked Questions about Peri-implantitis
Peri-implantitis can be painful and can also permanently affect health. We are happy to help you find a solution to the problem.
The symptoms of peri-implantitis can be
- Bleeding gums and pocket formation around the implant
- Gum and bone recession
- Bad breath
- Pain or discomfort from the implant
- Implant loosening and implant loss in the final stage
The most effective way is to improve the bacterial environment in the mouth.
According to studies, the frequency of inflammation on implants is 10 to 65%. In our practice, we very rarely see peri-implantitis as long as the patient follows the oral hygiene instructions and visits the dentist regularly for check-ups and prophylaxis.
The most reliable diagnostic method is still radiographic imaging. Dental films, panoramic images or CBCT X-rays can show bone loss very clearly.
Even before peri-implantitis is visible on the X-ray, a meaningful prognosis for peri-implantitis can be made using an a-MMP8 test.
Further information
The information listed includes relevant topics and is intended to provide a better understanding.