Gum Recession
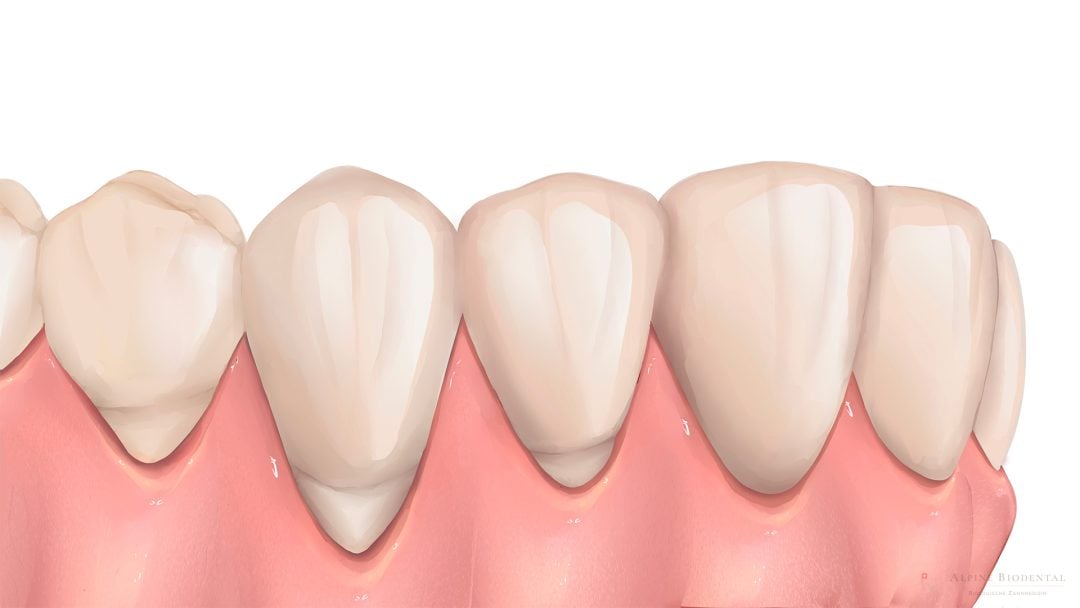
Gum recession, also known as gum atrophy, is a widespread issue, particularly affecting older individuals. In this condition, the gum tissue gradually pulls away, leaving larger portions of the teeth exposed and unprotected. The causes of gum recession can be diverse and often mutually reinforcing.
This article aims to provide information on gum recession and offer guidance on preventing further deterioration.
Understanding Gum Recession
Gum recession is a commonly occurring problem in the oral cavity, involving the gradual or rapid retreat of the gum tissue. This exposes the tooth roots, leading to various consequences for dental health.
Gum recession may result in aesthetic concerns, especially when a high smile line exposes the affected area in the front teeth. Stabilizing gum recession and protecting exposed teeth with appropriate measures can help maintain the situation without compromising oral health.
If you notice signs of gum recession, it is crucial to have the condition assessed and treated by an experienced dentist to ensure proper care.
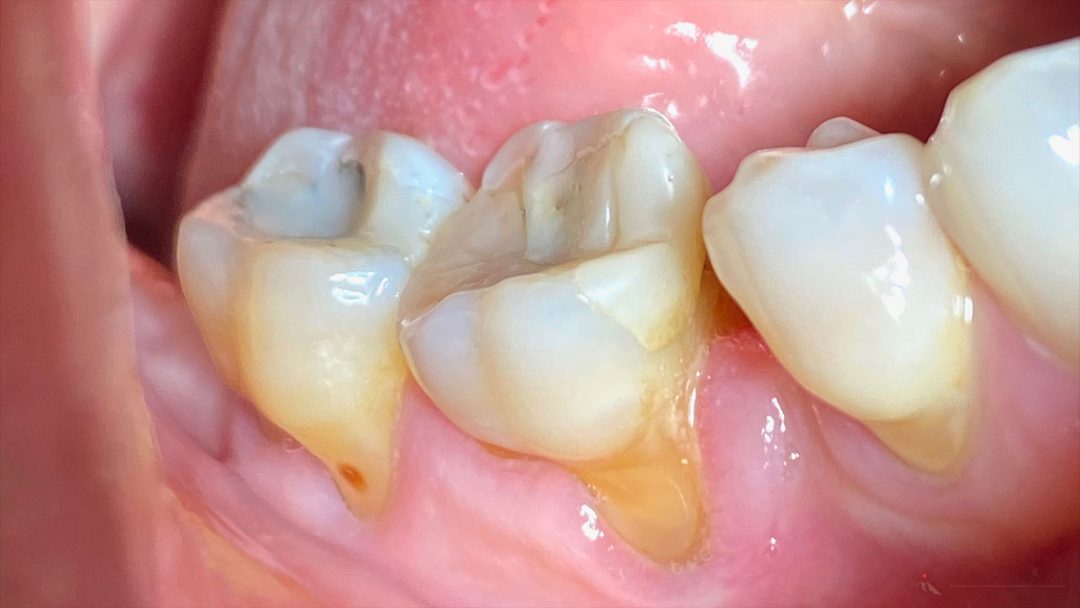
Symptoms of Gum Recession
The symptoms of gum recession are quite distinct: the gum tissue pulls back, causing the tooth to appear longer. Frequently, exposed tooth roots become visible, and sensitivity to cold or touch may increase.
Gum recession complicates oral hygiene, leading to more food particles getting trapped between the teeth. Consequently, areas with significant gum recession are more prone to gum inflammation and periodontitis.
With gum recession, there is always an associated loss of the underlying jawbone. Thus, it is invariably a combined recession of both gum tissue and bone. This results in a compromised tooth anchorage, potentially leading to tooth loosening and, in the long term, tooth loss.
Aesthetically, an unnatural gum line emerges with elongated tooth crowns. The harmonious interplay of pink aesthetics (gum tissue) and white aesthetics (teeth) is compromised. For further information, please refer to the article on dental aesthetics.
Causes of Gum Recession
Gum recession can have various causes, often involving a combination of factors that mutually reinforce the recession. If you are experiencing gum recession, it is crucial to understand the individual causes and determine which factors have contributed to the recession in your case.
Poor Oral Microbiota and Gum Recession
An unhealthy oral microbiota can lead to inflammation of the gums, periodontal ligament, and jawbone. If only the gums are affected, the condition is termed gum inflammation or gingivitis. When the inflammation spreads to the entire periodontal ligament, it becomes periodontitis.
Pathogenic bacteria nestle in the gum pockets, triggering a local immune response with persistent inflammation. This chronic inflammation ultimately results in the degradation of the jawbone and, consequently, gum recession. In cases of gum recession caused by harmful oral bacteria, the gums often appear red and swollen, and they tend to bleed easily upon touch or during brushing.
Improper Toothbrush and Incorrect Brushing Techniques
Over the years, many patients adopt incorrect toothbrushing techniques. Applying excessive pressure and using a toothbrush with firm bristles can traumatize the gums, leading to recession. It is advisable to use a very soft toothbrush and avoid excessive pressure. Even electric toothbrushes can exert unnatural pressure on delicate tissues, potentially contributing to gum recession. If opting for an electric toothbrush, choose a sonic toothbrush with an extra soft brush head.
Dental Floss and Interdental Brushes
Dental floss and interdental brushes apply significant pressure to the gum tissue between teeth, particularly affecting the interdental papilla. Repetitive injuries to this delicate papilla may cause it to recede, leaving behind unsightly black triangles between the teeth. These black triangles are aesthetically displeasing and serve as a common location for food debris. It is advisable to prevent the formation of black triangles by using proper flossing and interdental brushing techniques.
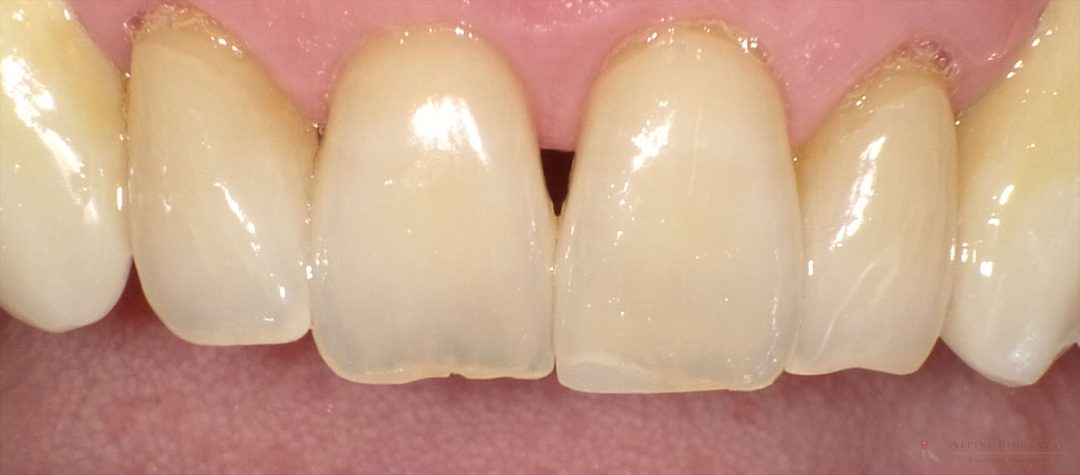
Gum Recession Due to Stress
Stress, in itself, cannot directly cause gum recession. However, mishandling stress can lead to detrimental effects. Many patients, when stressed, may start grinding their teeth, resulting in misalignments of the teeth, jaw muscles, and jawbone. Such misalignments not only contribute to gum recession but also lead to temporomandibular disorders (TMJ), with significant health consequences.
Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
Teeth grinding generates substantial forces in the jaw muscles, which are transmitted to the teeth. During this transmission of muscle forces, the teeth undergo slight bending. This microscopic bending occurs in the area of the gums where the tooth emerges from the bone. Consequently, enamel prisms break off, leading to wedge defects in the tooth and ultimately causing gum recession.
Orthodontics
When teeth are moved with aligners or braces, it is crucial to ensure there is sufficient bone tissue around the moving tooth. Gum recession may occur when teeth are moved outward, and the delicate bone fails to keep up with the movement. This results in the outer surface of the teeth (towards the lips or cheeks) being covered only by gum tissue, not bone. The gum-to-tooth connection is significantly weaker and more susceptible than the gum-to-bone connection. Over the years, this can lead to exposure of these anatomically incorrect areas.
Gum Recession Due to Vitamin Deficiency
Gum recession can be influenced by a vitamin deficiency, with Vitamin C and Vitamin D3 playing a significant role in gum health. Adequate amounts of these vitamins should be supplied. Many are familiar with the historical accounts of sailors developing a Vitamin C deficiency and losing their teeth, a condition known as scurvy. Scurvy is easily treated with Vitamin C supplementation, and it rarely occurs in modern times due to improved nutrition.
Gum Recession: What to Do?
Individuals affected by gum recession often wonder what steps to take. The first and foremost priority is to avoid anything that may have triggered gum recession. This approach can help halt further gum recession. For a precise analysis of individual causes, it is crucial to consult an experienced dentist.
Stopping Gum Recession
The initial step is to stop and prevent further gum recession. To achieve this, it is essential to identify and consistently avoid the factors that caused the recession.
If gum recession was triggered by an unhealthy oral microbiota, rebuilding the oral flora and placing a strong emphasis on it in the future is crucial. A healthy bacterial environment in the oral cavity is not only essential for gums but can also prevent issues like cavities and jaw inflammations.
In cases where using a too hard toothbrush with excessive force has been the cause in recent years, switching to a soft toothbrush is advisable, and brushing teeth with caution is essential. Traumatic use of dental floss and interdental brushes should be avoided, and instead, maintaining an optimal oral flora is emphasized.
Increased teeth grinding, misalignment due to excessive force, and past orthodontic treatments may require a thorough analysis of your bite. Precise clarification can be obtained during a TMJ consultation, involving a thorough examination of bite relations.
Once the individual cause of gum recession has been addressed, it is common for the gum to partially or fully recover. This is highly dependent on the underlying bone. If gum recession has been accompanied by increased bone loss, independent regrowth becomes challenging.
Gum Recession Treatment
After correctly identifying and avoiding the personal causes of gum recession, the situation is observed. If the gums cannot regenerate on their own, there are surgical interventions that can be performed by a dentist.
Various periodontal surgical methods can be employed to rebuild the gums. Effective techniques for gum recession include:
- Mucosal and connective tissue grafts
- Formation of mucosal flaps for coverage
- Envelope and tunnel techniques
- Semilunar technique
- Brushing technique with apical mattress sutures
- Combination with bone augmentation in complex situations
For all periodontal surgical procedures, we use A-PRF membranes and ozone, working atraumatically and minimally invasively. It is crucial that such methods be performed only by surgically experienced specialists.
Home Remedies for Gum Recession
There are no known home remedies that can reverse gum recession. However, some home remedies can help stop the progression of gum recession and stabilize the situation.
Firstly, a balanced diet is crucial to provide the gums with all necessary building blocks and cofactors. Adequate intake of Vitamin C and Vitamin D3, in particular, is essential for promoting gum health. Avoid excessive sugar consumption to prevent further promotion of harmful bacteria.
Rinsing with baking soda daily can buffer bacterial acids and reduce irritation of the mucous membrane and teeth.
Rinsing with anti-inflammatory teas, such as chamomile, sage, or thyme, soothes the gums and promotes a healthy oral environment.
Daily oil pulling is also a helpful method to strengthen the gums. You can use coconut or olive oil for this purpose.
Toothpaste for Gum Recession
There is no toothpaste that can stop or prevent gum recession. On the contrary, overly abrasive toothpaste can accelerate gum recession and should be avoided. The abrasive components in such toothpaste can cause small traumas to the gums and lead to the abrasion of tooth structure. Therefore, it is recommended to use toothpaste with a low RDA (Relative Dentin Abrasivity) value. Read more about toothpaste without fluoride in the article “Fluoride-Free Toothpaste“.
Dr. med. dent. Rebekka Hueber
Gum recession can have various causes that should be thoroughly investigated. Our team is here to assist you.

Frequently asked Questions about Gum Recession
Since gum recession has various causes and the reasons are not always clear, individuals affected by it often have various questions on the subject. We aim to provide comprehensive tips so that you can handle the problem as effectively as possible.
If the causes of gum recession have been eliminated, gums can partially or even fully regrow. However, whether regeneration occurs depends on the severity of the recession and the condition of the underlying bone. If the jawbone around the affected tooth has significantly receded, it is unlikely that the gums will fully regenerate.
Yes, it can occur when teeth are rapidly moved by orthodontic treatment with Invisalign® and the jawbone fails to grow accordingly. As a consequence, later on, the surrounding bone is missing in some tooth areas, and the gums no longer have good stabilization. In such cases, relief can only be achieved through periodontal surgery and bone augmentation.
Gum recession is not solely related to oral hygiene. There are other factors contributing to gum recession. Therefore, despite maintaining good oral hygiene, gum recession can still occur.
Gum recession on a tooth often indicates overload due to excessive force during tooth brushing. Use only very soft toothbrushes and brush your teeth in a way that does not harm the gums. A manual toothbrush should be preferred over an electric toothbrush, as electric toothbrushes can exert rapid and unnaturally high forces.
A thorough examination and proper treatment planning by an experienced dentist are essential.
Yes, gum recession is more common in older age because the gums are strained and traumatized over the years.
Further information
Relevant information is listed below to provide you with more insight.