NICO / FDOJ
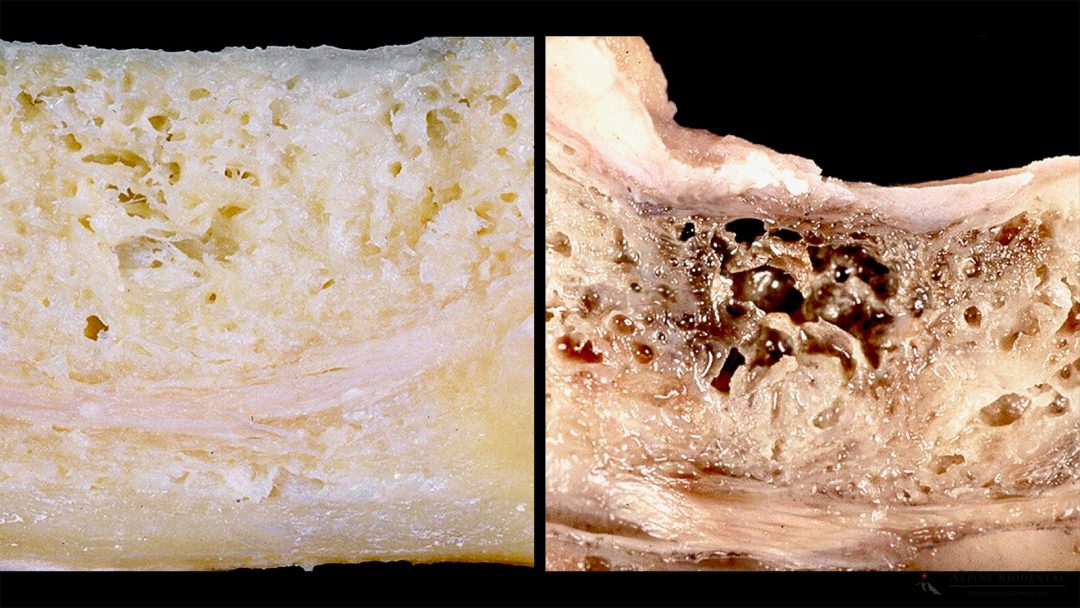
The clinical picture NICO or FDOJ refers to fatty, non-mineralized areas in the jawbone, which often develop after tooth removal and can represent a chronic burden on the body.
NICO stands for “Neuralgia Inducing Cavitational Osteonecrosis” and is also known in German-speaking countries as FDOJ “Fatty Degenerative Osteolysis of the Jaw Bone”. NICO and FDOJ therefore refer to the same clinical picture, which can represent an undetected inflammation (silent inflammation) in many patients.
NICO or FDOJ is sometimes also referred to as osteomyelitis, osteonecrosis or osteolysis of the jawbone.
Causes of NICO/FDOJ
NICO (Neuralgia-Inducing Cavitational Osteonecrosis) or FDOJ (Fatty degenerative osteonecrosis and osteolysis of the jawbone) typically occurs in the areas of the jawbone where a tooth, such as a wisdom tooth, has been removed in the past. Following a tooth extraction, the resulting void in the jaw must be replenished with fresh bone. Various factors often lead to incomplete bone formation, causing the affected area to fill not with healthy and mineralized bone but with fatty, inflammatory tissue.
Factors that contribute to NICO/FDOJ:
- Poor nutrition with insufficient essential components for bone healing.
- Deficiency in Vitamin D3.
- Premature removal of teeth during the growth phase. The body requires the building blocks for growth, neglecting bone healing.
- Body poisoning, hindering optimal bone healing.
- Impaired blood circulation at the wound site, which can be exacerbated by the use of adrenaline in the anesthetic.
Diagnosis of NICO/FDOJ
A preliminary diagnosis of NICO or FDOJ can be established through a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan. This three-dimensional X-ray imaging allows for a clear depiction of areas with low bone density.
An instrument specifically designed for diagnosing NICO/FDOJ is the CaviTAU® Ultrasound Diagnostic device. This tool enables precise visualization and detection of NICO/FDOJ.
Additionally, a blood test can determine the level of RANTES. RANTES is an inflammatory marker associated with this type of bone inflammation.
Impact on the Body
NICO/FDOJ produces significant amounts of a messenger molecule called RANTES. This inflammatory mediator is involved in many inflammatory conditions in the body and poses a health risk at higher concentrations.
RANTES has been proven to be linked to various conditions such as rheumatism, asthma, multiple sclerosis, migraines, multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS), chronic fatigue syndrome (ME-CFS), and some tumor diseases.
Treatment of NICO/FDOJ
Treatment involves only a careful but thorough surgical clearance of the affected areas. The surgery is complemented by ozone and APRF (Autologous Platelet-Rich Fibrin) and should be as atraumatic as possible.
The surgical treatment of NICO/FDOJ should only be undertaken after a precise and accurate diagnosis.
Dr. med. dent. Rebekka Hueber
FDOJ can cause health problems. A careful but thorough approach is important. We can help you further.

Further information
The further information is intended to give you a better overview of the subject area.